Table of Contents
Let’s be honest, parametric design sounds fascinating until you actually open the software and get hit with a maze of nodes, plugins, and prerequisites.
Whether you’re a designer exploring new creative tools, an educator looking for something more intuitive for students, or someone just trying to model without needing an engineering degree, you’ve probably found yourself wondering: “Is there a simpler, friendlier way to do this?”
Grasshopper 3D is a legend in the parametric world, no doubt, but it’s not for everyone. Some find it powerful yet overwhelming, especially with its tight dependency on Rhino and limited cloud features.
Thankfully, the design world has moved on. Today, there are tools that are just as smart but far more accessible, whether you’re into generative visuals, product design, architecture, or collaborative workflows.
Here’s a carefully curated list of the top 10 alternatives to Grasshopper 3D. Each tool offers its own unique advantages, community, and learning experience. Some are free, some run in the cloud, and one might just become your new favorite.
1. BeeGraphy
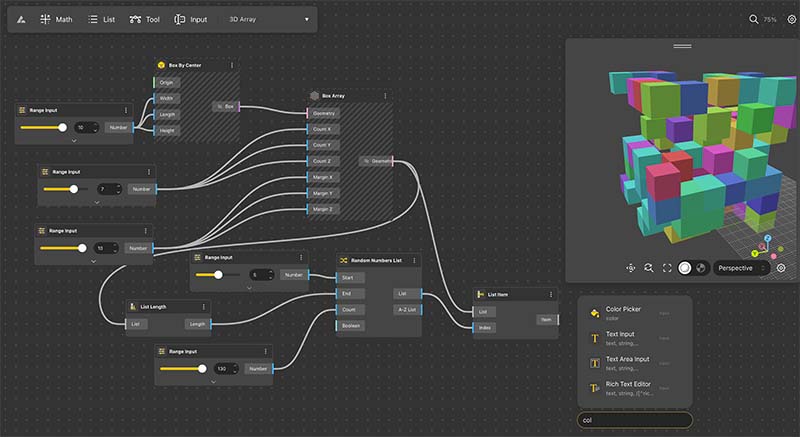
BeeGraphy’s browser-based parametric design tool showing a 3D array generated with range inputs, random values, and transformation matrices.
Who It’s For: ,Parametric designers , Product configurator developers, educators creating parametric templates, designers selling models through a digital marketplace.
Why Choose BeeGraphy?
If you’re looking for a modern, browser-based parametric design tool that supports real-time collaboration, BeeGraphy can be your go-to parametric design tool, a simpler and more collaborative alternative to Grasshopper 3D. It’s intuitive, cloud-based, and designed for seamless team workflows, perfect for studios or remote work. Beegraphy also has a marketplace where designers can list their models and earn money through that. The product confiugrator also helps business to integrate 3d models on their website which can be customisable as well.
Why It Stands Out: BeeGraphy is a web-based platform designed to make parametric design more approachable and collaborative. Unlike traditional tools that require downloads and complex setups, BeeGraphy runs directly in your browser. This makes it ideal for remote teams or educators who need a lightweight, flexible design solution.
Key Features:
- Real-time collaborative design sessions.
- User-friendly BeeGraphy Editor.
- Extensive library via BeeGraphy Market.
- Access to BeeGraphy Tutorials
- Developer-friendly API integrations.
Use Cases:
- Customizable 3d models sold via digital storefronts
- Interactive parametric templates for classrooms
- Remote teams co-developing 3D prototypes
2. Dynamo (Autodesk Revit)

A Dynamo script showcasing an automated workflow for creating Revit revisions, Image Source: Dynamo
Who It’s For: Architecture professionals working with BIM, Revit-centric studios, infrastructure and MEP consultants
Why Choose Dynamo?
Dynamo is your go-to tool for visual programming within Autodesk Revit. Whether you’re automating tasks or generating complex geometry, its node-based environment is ideal for integrating parametric design into BIM workflows.
Why It Stands Out: Dynamo works directly within Autodesk Revit, allowing architects and engineers to automate tasks and generate complex geometry using logic-based workflows. It’s especially useful in large-scale architectural projects where precision and data integration are critical.
Key Features:
- Visual programming directly inside Revit
- Python scripting support
- Rich community libraries
- BIM-specific parametric logic
Use Cases:
- Parametric placement of lighting or windows
- Adaptive facades based on site data
- Energy and daylighting simulations
3. Blender (Geometry Nodes & Sverchok)
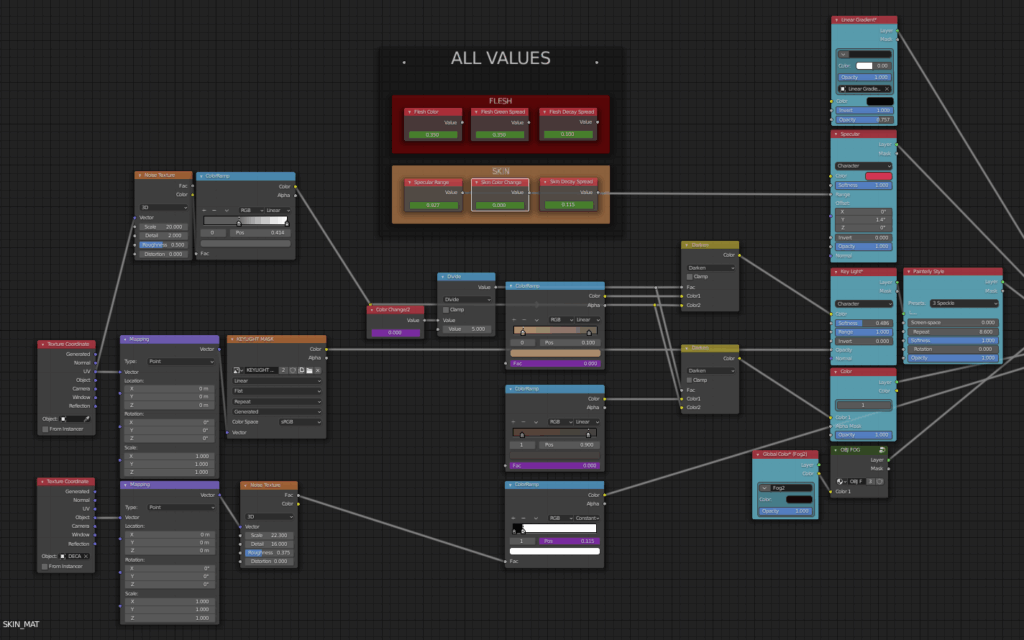
A detailed Blender node graph for creating procedural skin and flesh materials, showcasing a node-based workflow as a creative alternative to Grasshopper for shader design and material manipulation.Image Source: Blender
Who It’s For: Digital artists, creative technologists, experimental product designers
Why It Stands Out: Blender is already known for its powerful 3D modeling and animation capabilities. With the addition of Geometry Nodes and the Sverchok plugin, it transforms into a capable parametric design tool. Its open-source nature makes it an excellent choice for experimentation and customization.
Key Features:
- Geometry Nodes for procedural modeling
- Sverchok for logic-based design
- Integrated rendering and animation tools
- Python scripting compatibility
Use Cases:
- Generating procedural architectural facades
- Creating dynamic NFT artworks
- Modeling kinetic sculptures
4. Houdini (by SideFX)
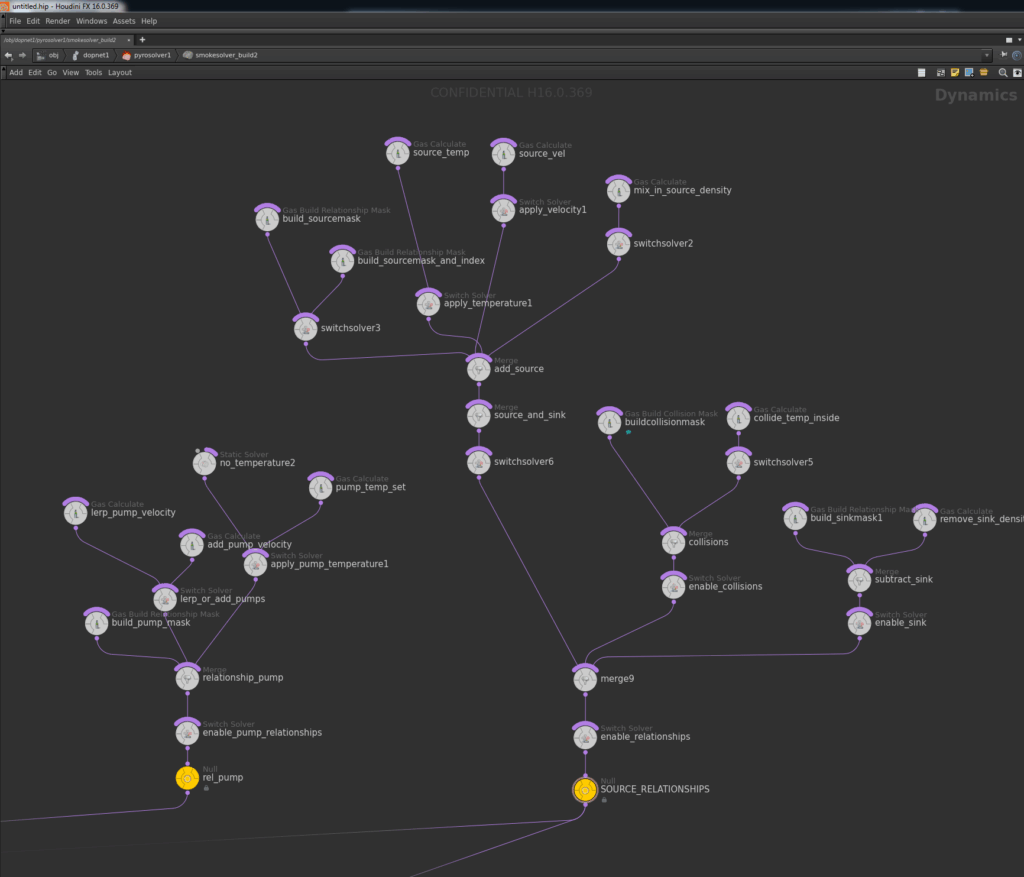
This Houdini node graph illustrates a complex dynamics setup involving temperature, velocity, and collision systems. Image Source : Side Fx
Who It’s For: VFX studios, simulation artists, generative design researchers
Why Choose Houdini?
Houdini is the heavyweight of procedural modeling and simulation. Its node-based system allows for complex generative geometry and real-time iterations, ideal for advanced users who value flexibility and depth.
Why It Stands Out: Houdini is revered in the visual effects industry for its node-based approach to procedural generation. Its simulation tools make it a favorite for creating everything from realistic smoke to algorithmic cityscapes. For architecture, it’s ideal for complex systems and responsive forms.
Key Features:
- Fully procedural node-based workflows
- Physics, particle, and fluid simulation tools
- Reusable digital assets (HDAs)
Use Cases:
- Simulating environmental effects for urban design
- Generating abstract structures for art installations
- Modeling erosion-driven landscapes
5. TouchDesigner
Fusion 360 view of a detailed mechanical CAD assembly with parametric parts.Image Source – Toucher Desinger UI
Who It’s For: Interactive artists, AV performers, experience designers
Why Choose TouchDesigner?
Looking to build real-time generative visuals or interactive installations? TouchDesigner is a powerful visual programming tool that combines parametric logic with multimedia and hardware integration.
Why It Stands Out: TouchDesigner focuses on creating interactive and real-time generative content. It’s a go-to for anyone working in live visuals, installations, or multimedia performances.
Key Features:
- Live node-based programming
- Integration with sensors (OSC, MIDI, etc.)
- Real-time audio-reactive content
Use Cases:
- Interactive museum installations
- VJing and stage visuals
- Audiovisual algorithmic art
6. Marionette (Vectorworks)
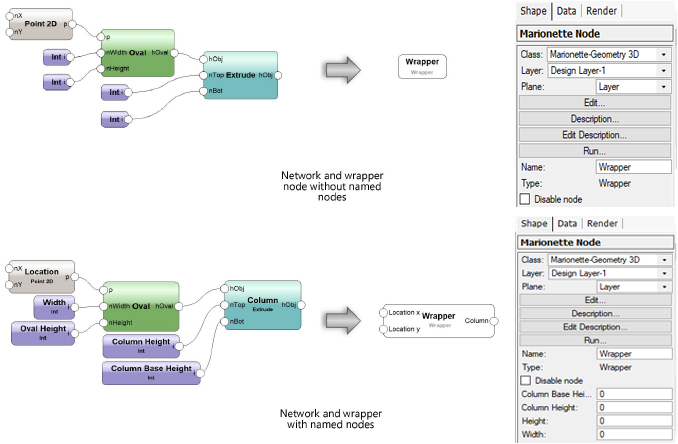
This image showcases a node-based visual scripting editor, where design logic is constructed using interconnected nodes to define parameters, geometry, and workflows. Image Source : Vectorworks
Who It’s For: Landscape designers, Vectorworks users, architects using BIM
Why Choose Marionette?
Marionette is a built-in graphical scripting tool in Vectorworks. It’s perfect for automating design tasks, creating smart BIM objects, and building reusable parametric systems without needing to write code.
Why It Stands Out: Built into the Vectorworks environment, Marionette enables visual scripting without needing to write code. It’s particularly effective for creating parametric BIM elements and automating repetitive workflows.
Key Features:
- Drag-and-drop scripting interface
- Optional Python scripting
- Works with BIM data and smart objects
Use Cases:
- Automating path layouts in landscape designs
- Creating data-driven urban modules
- Smart object generation for BIM workflows
7. OpenSCAD

A visual node-based editor in OpenSCAD Graph Editor used for defining CNC toolpaths and generating G-code through connected parameter nodes.Image Source: OpenScad
Who It’s For: Hardware developers, engineers, version-control-driven makers
Why Choose OpenSCAD?
Unlike node-based or GUI-driven tools, OpenSCAD lets you write code to generate models. It’s ideal for 3D printing parts or precise engineering designs with parametric control through scripting.
Why It Stands Out: OpenSCAD is a script-only modeling tool that excels at logic-based design. It’s highly reproducible and integrates well with version control systems, making it popular among developers.
Key Features:
- Fully code-based modeling
- Great for version control and reproducibility
- Lightweight and cross-platform
Use Cases:
- Creating customizable hardware parts
- Developing reusable 3D printing templates
- Designing with exact measurements for mechanical systems
Choose the Right Compass for Your Creative Map
Finding the ideal alternative to Grasshopper 3D doesn’t have to be complicated. The key is understanding your own design needs and matching them with a tool that aligns with your goals. Are you working on highly complex generative designs and simulations? Or do you need a lightweight, intuitive tool that helps you build customizable 3D models with ease?
Each tool featured in this guide serves a different purpose. From BeeGraphy’s cloud-based collaboration and product configurator flexibility to Houdini’s simulation-rich generative workflows, and Blender’s open-source artistic potential – the right choice depends on your workflow, skill level, and the kind of work you aspire to create.
Remember, no single software will suit everyone. What matters most is how well the tool complements your creative rhythm, the kind of projects you handle, and the speed at which you need to iterate. If you’re still experimenting or trying to find a new groove beyond Grasshopper, try one or two of these tools and get hands-on. Many of them are free or offer trial versions, so you have room to explore before you commit.
Already using one of these Grasshopper alternatives? We’d love to hear your take. Share your experiences, tips, or even your frustrations in the comments – your insights could be just what another designer needs to make the switch confidently.
Happy designing!