Table of Contents
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, it’s transforming the way we design, manufacture, and even think about everyday objects. From groundbreaking materials to revolutionary applications, join us as we uncover the top 3D printing trends that are redefining the future of this dynamic field.
Stay tuned to discover how these advancements are not only revolutionizing manufacturing processes but also empowering individuals and businesses to bring their creative visions to life like never before.
Expansion of 3D printing
The 3D printing industry continues to experience significant growth and innovation. Some key trends and developments in the industry include:
- Expansion of materials: The range of materials available for 3D printing has expanded beyond plastics to include metals, ceramics, and even biological materials. This has opened up new possibilities for various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
- Improved speed and efficiency: Advancements in 3D printing technology have led to faster printing speeds and increased efficiency, making it more viable for mass production and reducing the time it takes to bring products to market.
- Greater precision and accuracy: 3D printers are becoming more precise and accurate, allowing for the production of intricate and complex designs that were previously impossible or difficult to achieve.
- Widespread adoption: 3D printing is becoming more accessible and affordable, leading to increased adoption across various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and healthcare.
- Sustainability: The 3D printing industry is focusing on sustainability by reducing waste and using eco-friendly materials. This is particularly important as environmental concerns become more prominent.
- Customization and personalization: 3D printing allows for greater customization and personalization of products, enabling companies to cater to individual customer needs and preferences.
Overall, the 3D printing industry is experiencing significant growth and innovation, with new applications and technologies emerging regularly. This is expected to continue as the technology becomes more advanced and accessible.
In what areas is 3D printing currently used?

Photo by ZMorph All-in-One 3D Printers
3D printing technology has enabled several previously unthinkable ideas to become a reality across various industries. Some notable examples include:
- Bioprinting: The ability to 3D print living tissues and organs has the potential to revolutionize healthcare. Researchers are now able to create functional human tissues, such as skin, blood vessels, and cartilage, which can be used for transplantation, drug testing, and medical research.
- Customized prosthetics and implants: 3D printing has allowed for the creation of customized prosthetics and implants that are tailored to an individual’s unique anatomy. This has improved the comfort, functionality, and aesthetics of these devices, leading to better patient outcomes.
- Complex architectural structures: 3D printing has enabled architects and engineers to design and create complex structures that were previously impossible or extremely difficult to build using traditional construction methods. This includes intricate lattice structures, curved surfaces, and even entire buildings.
- Lightweight aerospace components: The aerospace industry has benefited from 3D printing’s ability to create lightweight, complex, and high-strength components. This has led to reduced fuel consumption and increased efficiency in aircraft and spacecraft.
- Customized consumer products: 3D printing has allowed for greater personalization and customization of consumer products, such as jewelry, clothing, and accessories. Customers can now have unique, one-of-a-kind items that are tailored to their preferences and needs.
- Food printing: 3D printing technology has been applied to the food industry, enabling the creation of intricate and customized food items. This includes printed chocolate, pasta, and even plant-based meat alternatives.
- Preservation of cultural heritage: 3D printing has been used to recreate and preserve historical artifacts and monuments that have been damaged or destroyed. This helps to maintain cultural heritage and allows for the study and appreciation of these important pieces.
These are just a few examples of how 3D printing technology has transformed various industries and made previously unthinkable ideas a reality. As the technology continues to advance, it is likely that even more innovative applications will emerge.
How has 3D printing changed manufacturing and commerce?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has the potential to fundamentally transform both manufacturing and commerce in a number of ways. Here are a few examples:
- Customization: 3D printing enables the creation of highly customized products on-demand. This can lead to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty, as well as new business models such as personalized products and mass customization.
- Design innovation: With 3D printing, designers can create highly complex geometries and intricate details that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing processes. This can lead to new design possibilities and innovative products that were previously not feasible.
- Reduced waste: 3D printing is an additive process, which means that material is only added where it is needed. This can result in significant reductions in material waste compared to traditional manufacturing processes.
- Distributed manufacturing: 3D printing enables the creation of products on-demand, close to where they are needed. This can reduce transportation costs and lead times, as well as enable new business models such as distributed manufacturing and micro-factories.
- Intellectual property protection: 3D printing can make it more difficult to protect intellectual property, as it is easier to replicate products and designs. However, it can also enable new forms of protection, such as watermarking and encryption.
Overall, 3D printing has the potential to disrupt traditional manufacturing and commerce in a number of ways. By enabling customization, design innovation, reduced waste, distributed manufacturing, and new forms of intellectual property protection, it is likely to have a significant impact on a wide range of industries in the years to come.
What do 3D printing statistics show?
Extensive market research and analysis have highlighted the significant growth of the 3D printing industry.
As reported by Statista, the global 3D printing industry was valued at approximately $12.6 billion in 2020, marking a considerable increase from the market size of $8.8 billion in 2017.
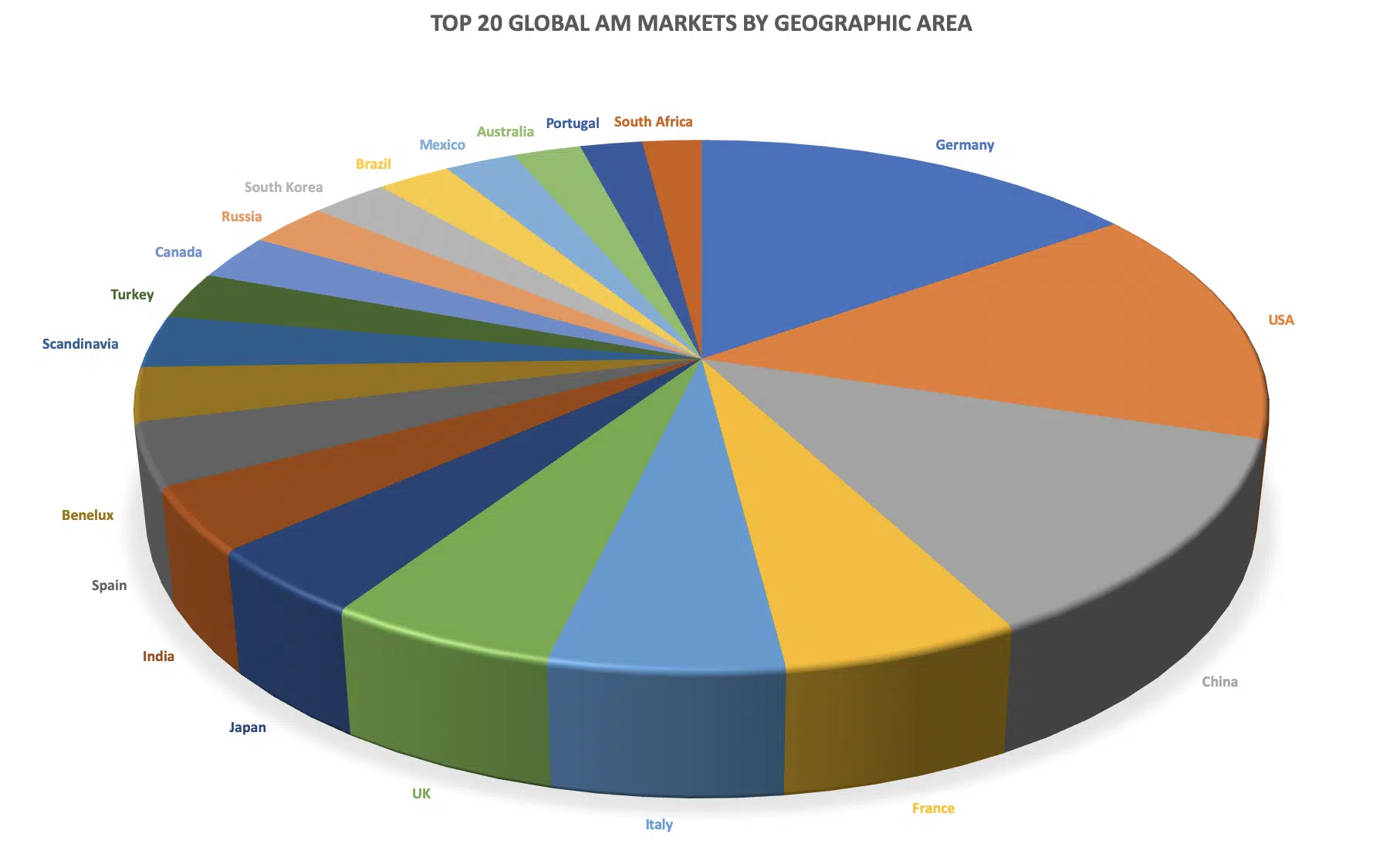
The top 20 global AM markets. Source: 3dpbm elaboration of SmarTech Analysis data (data in millions of US dollars). Source: www.3dprintingmedia.network
The top 20 additive manufacturing markets are mainly located in the Americas, Europe, and Asia, according to data published in 2020 by additive manufacturing media company 3D Printing Media Network (3dpbm) and SmarTech Analysis.
A survey conducted by Jabil, a prominent manufacturing services company, revealed that over 300 representatives of manufacturing companies primarily use 3D printing for research and development, followed by prototyping, custom-made tools, low-volume manufacturing, parts production, and repair.
Additionally, over 66% of respondents reported that 3D printing is faster than traditional manufacturing methods.
The most commonly used 3D printing materials include plastics, ceramics, metals, Multicolore/sandstone, constituent materials, resins, and wax. Fused deposition modeling (FDM)/fused filament fabrication (FFF) is the most utilized 3D printing technology in 2021 (71%), according to Statista, followed by selective laser sintering (SLS) (42%).
The 3D printing market size on a global scale is estimated to reach $62.79 billion by 2028. The Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) is supposed to be 21% from 2021 to 2028. Given the interest in metal 3D printing from the automotive, aerospace, and defense industries, the metal segment is expected to overtake polymer in the following seven years.
An emerging and promising segment in the field is ceramic 3D printing. Market research and business intelligence company IDTechEx predict that by 2032 ceramics 3D printing will hit $400 million.
Parametric modeling in 3D printing
Parametric modeling is a powerful technique used in 3D printing that allows for the creation of complex and precise geometries. This approach involves using mathematical equations to define the shape and dimensions of a model, allowing for the easy modification of design parameters such as size, shape, and orientation.

In 3D printing, parametric modeling enables the creation of designs that can be customized to specific needs or requirements. For example, by adjusting the parameters of a parametric model, it is possible to quickly create variations of a product that differ in size, shape, or material properties.
Parametric modeling is particularly useful for 3D printing because it allows for the creation of highly detailed and precise models that would be difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. With 3D printing, designers can create highly complex geometries and intricate details that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing processes.
Overall, parametric modeling is a valuable tool for 3D printing that enables the creation of highly customizable and precise designs that can be easily modified and optimized for specific manufacturing needs.
Benefits of using parametric modeling for 3D printing
- Customization: With parametric modeling, designers can easily create models that can be customized to specific needs or requirements. This allows for greater flexibility and the ability to quickly adjust and optimize designs.
- Precision: Parametric modeling enables the creation of highly detailed and precise models that can be easily modified and refined. This can result in higher quality prints with greater accuracy and consistency.
- Efficiency: With parametric modeling, designers can easily generate multiple variations of a design without having to manually create each version. This can save time and increase efficiency in the design process.
- Design optimization: Parametric modeling allows for the optimization of designs based on specific manufacturing parameters, such as material properties, print speed, or resolution. This can result in more efficient use of resources and improved product performance.
- Cost savings: By optimizing designs and minimizing material waste, parametric modeling can lead to cost savings in the manufacturing process. Additionally, the ability to quickly iterate and test designs can also save time and resources.
- Accessibility: Parametric modeling software is often free or low-cost and widely available, making it more accessible to a broader range of designers and manufacturers. This can lead to greater innovation and creativity in the 3D printing industry.
How BeeGraphy can assist 3D printing specialists?

BeeGraphy, an online computational design software, can be highly beneficial to 3D printing specialists in several ways. Here are a few examples:
- Design automation: BeeGraphy can automate the design process, allowing 3D printing specialists to quickly generate complex and optimized designs without manual intervention. This can save significant time and effort, as well as improve design quality and consistency.
- Parametric modeling: BeeGraphy enables the use of parametric modeling techniques, allowing 3D printing specialists to quickly adjust design parameters and iterate on designs in real-time. This can facilitate the creation of highly customized and optimized designs for 3D printing.
- Material optimization: BeeGraphy can help 3D printing specialists optimize designs for specific materials and printing processes. By simulating how materials behave under different conditions, BeeGraphy can help ensure that designs are optimized for strength, durability, and other performance factors.
- Collaboration: BeeGraphy is a cloud-based software that enables collaboration and sharing of designs with team members and clients. This can facilitate communication and feedback, as well as streamline the design process.
Overall, BeeGraphy can assist 3D printing specialists by automating the design process, facilitating parametric modeling, optimizing designs for materials and printing processes, and enabling collaboration and sharing of designs. By leveraging these capabilities, 3D printing specialists can improve design quality, reduce time to market, and create highly customized and optimized products for their clients.
Register your account on BeeGraphy and start using the free online computational design software for creating amazing parametric models solo or with your teammates.